Digital Transformation: The New Engine of the Automotive Industry
Once dominated by mechanics and engineering, the automotive industry is now in the midst of a profound transformation. In a world where software and data play an increasingly important role, traditional manufacturing methods are no longer sufficient. The digital transformation has become the new engine of the industry, setting new standards for efficiency, innovation, and personalization.
But this revolution also brings with it significant challenges. How can data be comprehensively digitized? How can efficient processes be implemented? And most importantly, how do you get all stakeholders to embrace this digital culture? Addressing these questions is crucial for future success in the industry.
In this article, we will take an in-depth look at the challenges of digitization in the automotive industry. We’ll analyze the different phases of this change, the obstacles to overcome, and the opportunities that arise. You will learn how digital technologies can optimize the design, production, and maintenance of vehicles while improving quality and safety.
Whether you’re an industry expert or simply a technology enthusiast, this article will give you an insight into the challenges and perspectives of digital transformation in the automotive industry.

Digital Transformation in the Automotive Industry
The digital transformation of the automotive industry is not a one-off project but a continuous process that is redefining the entire value chain. Closely linked to the concept of Industry 4.0, this change is structured into three central, sequential phases. To create a fully networked ecosystem, it is crucial to tackle these steps one after another:
The Three Phases of Change:
- Data Digitization (The Paperless Office): Paper-based data is converted into usable digital data.
- Implementation of Efficient Processes: Production, design, and maintenance processes are optimized using digital tools.
- Establishment of a Digital Culture: The acceptance of digital tools and working methods is promoted among all employees.
This transformation has been and continues to be driven by several key factors that serve as the foundation of the digital ecosystem:
- Big Data: The collection, digitization, and analysis of large amounts of data for optimal use.
- Cloud (Computing): The provision of a network of servers and applications that is accessible anytime and anywhere.
- Simulation: The creation of virtual models (digital twins) to evaluate the performance of products in advance.
- System Integration: The exchange of information between different IT systems is facilitated and promoted, breaking down silos and improving collaboration.
- IoT (Internet of Things): Sensors and cameras connected to the internet optimize production and safety.
- Cybersecurity: Crucial for protecting intellectual property and sensitive data from cyberattacks.
- Augmented Reality: Enables the interactive visualization of products in their real environment, simplifying design and maintenance processes.
- Autonomous Robots: Used for repetitive and complex tasks—often in challenging environments—they can perceive their surroundings.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: Enable the analysis of data and the automation of certain tasks.
All these factors form a comprehensive digital ecosystem that revolutionizes not only design and production but also the entire product life cycle. This networked approach allows companies in the automotive industry to act with flexibility efficiency, and innovation. Those who use these technologies strategically secure a crucial competitive advantage in the future of mobility.
In Practice: The Challenges of an Automotive Part in Every Production Phase
Let’s approach the topic with a practical example: your vehicle’s seat. How was it developed and manufactured? From design to FMEA, the validation plan, and laboratory tests, all the way to series production, every phase is crucial.
- Design: The initial design and conception phase must be guided by legal and safety requirements in the market.
- FMEA (Failure Mode and Effects Analysis): Ensures the product’s compliance with all relevant requirements.
- Validation Plan (DVP&R): Confirms simulations and validates the design.
- Test Laboratory: Tests and characterizations to check for conformity.
- Production: Series production and product life cycle management.
- Quality: Centralization of information, document management, audits, and problem-solving.
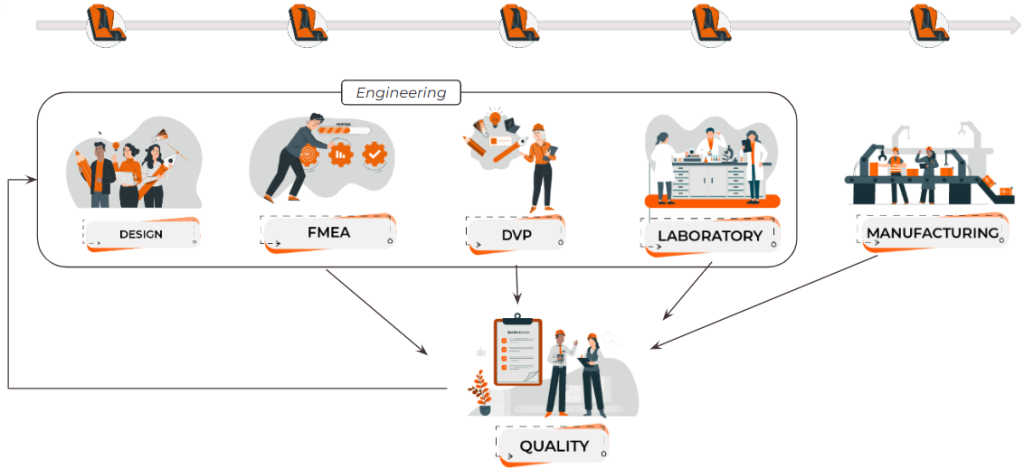
Each of these phases generates a significant amount of data that requires efficient management and comprehensive data integrity to optimize the product’s production, quality, and maintenance. The digitization of these processes is therefore of crucial importance for competitiveness in the automotive industry. Let’s take a closer look at each of these steps.
The Design Phase
The digital transformation has a profound impact on the design phase in the automotive industry.
- Input: Regulatory and safety requirements (standards, legislation) influence the conception and design of the products.
- Output: With comprehensive digitization, structured data can be generated, such as:
- Bills of Materials (BOMs)
- IMDS Data (International Material Data System)
- CAD Files (Computer-Aided Design) for mock-ups and additive manufacturing, which enables the optimization of components (individual sub-assemblies).
This area is primarily based on:
- Data Storage (Data Lake): A central storage location for all types of raw data.
- Artificial Intelligence: For simulation and condition monitoring of parts, to predict their behavior in the final environment (e.g., a seat in a vehicle).
Comprehensive digitization of the design phase optimizes conception, reduces costs, and accelerates the development of innovative products.
FMEA (Failure Mode and Effects Analysis)
After the design phase is completed, there is often a direct transition to FMEA. This crucial step is based on the specific requirements defined during the design phase, as well as the functional analysis of the product. In the automotive context, it is particularly important to ensure strict compliance with the AIAG VDA standard and the execution of the well-known 7 FMEA steps, which can be fully covered with BASSETTI’s software solutions.
FMEA therefore has:
- Input: Specific requirements (customer requirements, regulatory specifications) and the functional analysis of the product.
- Output: A control plan for production, as well as aligned product FMEA and process FMEA.
The comprehensive digitization of FMEA enables the automation of data flows, improves consistency between product and process FMEAs, and ensures compliance with regulations, particularly in accordance with the recommendations of APQP (Advanced Product Quality Planning).
The Verification Plan (DVP&R)
The DVP&R (Design Verification Plan & Report) primarily serves to confirm the accuracy of simulations and to make necessary adjustments to ensure product conformity. The DVP&R can be used in different phases:
- Before Design: To guide product development.
- After Design: As part of quality management, to identify the root causes of defects and initiate necessary corrective or preventive actions.
The DVP&R can therefore influence both the product and the manufacturing process. It is based on data from the preceding steps (design, FMEA, etc.) and in turn generates the following outputs:
- Validation reports
- Experience reports
- Test matrices for the laboratory
This step ensures the transition to laboratory tests and guarantees the robustness of the final product.
The Test Laboratory
Test laboratories play a crucial role in the automotive industry. To ensure the reliability and conformity of products, these labs must:
- Be Certified: They must comply with strict ISO standards (including ISO 17025) in their operations.
- Manage Resources: Human and material resources must be optimally allocated.
- Plan Efficiently: Artificial intelligence can be used to optimize and automate test planning.
- Create Comprehensive Reports: AI generates summary reports that facilitate the capture, storage, use, and provision of results for customers.
Therefore, the data that flows through the lab is primarily:
- Input: Test requests that the lab receives from the DVP (Verification Plan), design, and regulatory requirements (automotive standards).
- Output: Test reports, resource qualifications, and planning data.
Production, in turn, heavily depends on the lab’s results. Only when all tests are validated can the product be manufactured. The data originating from the design phase is then used to set up the necessary equipment and tools for series production. This synergy between the lab and production is crucial for ensuring the quality and efficiency of the manufacturing chain.
Production
The production of automobile manufacturers and suppliers generates a constant flow of data. It is therefore essential to control and utilize this information to optimize the entire process.
Production therefore receives:
- Input: All data from the design phase, as well as bills of materials, information on machines and tools, etc.
- Output: Various KPIs, maintenance data, and planning overviews.
Production generates a constant data flow, particularly production metrics such as Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE), production plans, and adherence to the schedule for the final assembly line. A seamless capture and monitoring of production times is essential. The precise calibration of equipment and the efficient management of upstream and downstream elements like logistics and personnel are also of crucial importance.
Quality Management
Quality Management (QM) can be described as the overarching nervous system of automotive production, which must be in constant communication with all previous phases. It ensures that every step in the design and manufacturing process meets the highest standards and exceeds customer expectations. In an industry where safety and reliability are paramount, comprehensive and data-driven quality control is indispensable.
The data flow in quality management can be divided as follows:
- Input: Data from production, test results, and regulatory requirements.
- Output: Quality reports, plans for corrective actions, and the tracking of non-conformities.
The Quality Management department centralizes all information, manages documents, conducts audits, and resolves problems. Digitization enables the automation of non-conformity tracking, improves traceability, and ensures compliance with quality standards.
The TEEXMA for Quality solution from BASSETTI is fully aligned with automotive standards such as IATF 16949, AIAG, and VDA. It directly addresses the challenges by supporting quality methods like APQP/PPAP, FMEA and Control Plan, 8D problem-solving, Layered Process Audits, and more. This robust integration allows automotive companies to effectively define, analyze, and anticipate risks, manage complex systems and supply chains, and automate problem-solving with AI.
TEEXMA: The Comprehensive Software Platform for Digital Transformation in the Automotive Industry
Digitization is not an optional upgrade but a fundamental redesign of the entire product life cycle in the automotive industry. The seamless management of the resulting data streams is the key to greater efficiency, better quality, and faster innovation cycles.
Given the increasing complexity of digitization in the automotive industry, the software platform TEEXMA proves to be a strategic partner. It offers a complete solution for managing and optimizing every step in the life cycle of an automotive component, from design to production, testing, and quality assurance. Thanks to its modular design, each solution can be used individually or in combination on the same platform. With TEEXMA, you can centralize and structure your data, automate your information flows, and facilitate collaboration between your teams. This ensures flawless regulatory compliance, optimizes your planning and maintenance, and allows you to fully leverage artificial intelligence for analysis and forecasting.
Do you or your company have a challenge in one or more of the areas mentioned? Learn more about our software platform TEEXMA and our individual solutions for the automotive industry here, or contact our experts directly.
